Home / Blog / Volumetric Adsorption Analyzer: A Key Tool for Surface Area Measurement
Volumetric Adsorption Analyzer: A Key Tool for Surface Area Measurement
29 10 月, 2025From: BSD Instrument

🔬 What is a Volumetric Adsorption Analyzer?
⚙️ How Does It Work?
Sample Preparation: The solid sample is degassed (heated under vacuum) to remove any pre-adsorbed gases or moisture.
Adsorption Measurement: The sample is cooled (usually to 77 K), and incremental amounts of gas (e.g., N₂) are introduced into the system. The gas pressure is monitored as it equilibrates with the adsorbed phase on the sample surface. The volume of gas adsorbed is measured at various pressures.
Data Analysis: Using the adsorption isotherm (a plot of the amount of gas adsorbed vs. relative pressure), sophisticated algorithms (like the BET method) calculate: Specific Surface Area Pore Volume Pore Size Distribution
🧪 Common Techniques Used
BET Surface Area Analysis (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller): Measures specific surface area by analyzing the linear portion of the adsorption isotherm at low relative pressures. Assumes multilayer adsorption of gas molecules.
Langmuir Model: Models monolayer adsorption; useful for certain non-porous or microporous materials.
BJH or DFT Methods: Used to determine pore size distribution from the adsorption-desorption isotherms. BJH (Barrett–Joyner–Halenda) is widely used for mesopores. DFT (Density Functional Theory) provides more accurate results across a broader pore size range.
✅ Key Applications
Catalysis: Characterization of catalysts and supports. Pharmaceuticals: Determination of surface properties of drug carriers. Energy Storage: Analysis of battery electrodes and supercapacitors. Environmental Science: Study of adsorbents like activated carbon. Materials Science: Development and testing of porous materials like MOFs, zeolites, and aerogels.
🎯 Why is Surface Area Important?
Surface area is directly related to the reactivity, adsorption capacity, and efficiency of many materials. High surface area often implies greater interaction sites for reactions, adsorption, or catalysis. Precise measurement ensures optimal material design and performance in industrial applications.
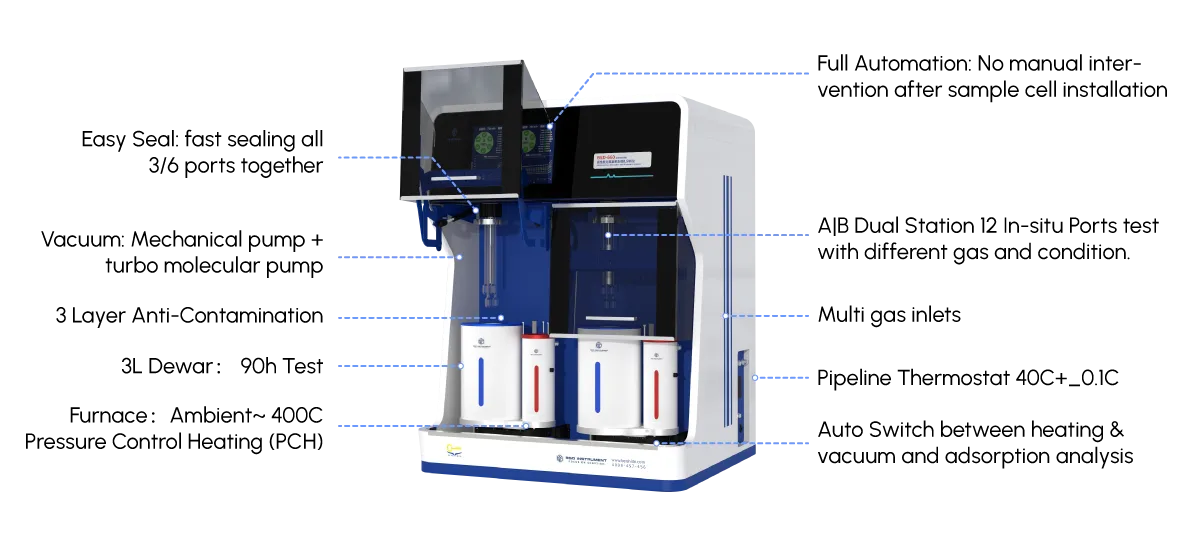
🛠️ Features of Modern Volumetric Adsorption Analyzers
High precision pressure sensors Automated degassing stations Low-temperature cryostats (for N₂ adsorption at 77 K) Software for advanced data analysis (BET, BJH, DFT) Compatibility with various adsorbates (N₂, Ar, CO₂, etc.)
🏁 Summary
Our Latest Blog & Articles
Stay updated with our latest news. Discover new product launches, innovative technologies, and upcoming events. Join our community and stay informed about all things lab equipment.
-
4 2 月, 2026
How Pore Size Analyzers Enable Breakthroughs in Catalyst and Battery Research
-
16 1 月, 2026
Advanced Applications of BET Adsorption Instrument in Nanomaterial Characterization
-
6 1 月, 2026
Advanced Characterization of Porous Materials Using a BET Adsorption Analyzer: Principles and Applications
-
29 12 月, 2025
Static Adsorption Mechanisms: A Comprehensive Review of Theoretical Models