Home / Product / BSD...
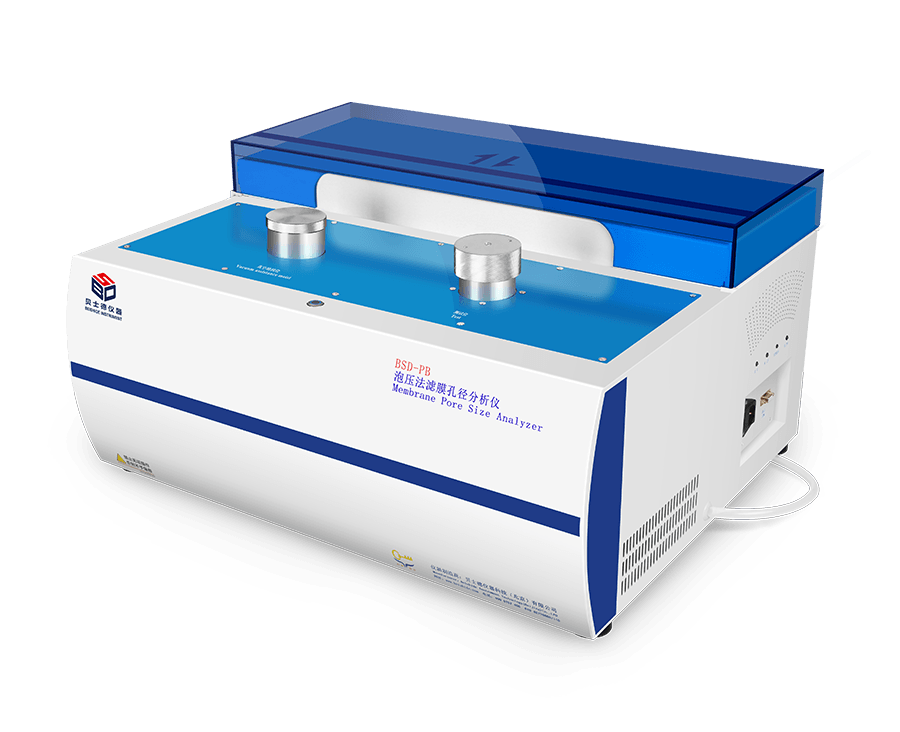
BSD- PBL Membrane Pore Size Analyzer Liquid-Liquid
The PB Membrane Pore Size Analyzer utilizes the gas-liquid or liquid liquid displacement method (bubble pressure method) to accurately measure the pore size characteristics of membrane materials. By applying a pressure difference across the membrane, the system overcomes the surface tension of the infiltration liquid, driving it through the pores to determine pore throat sizes. This method is the standard for ASTM thin film pore size testing. The analyzer is widely used for pore size analysis in materials such as filter membranes, fiber membranes, filter elements, battery separators, fabrics, non-woven fabrics, paper, ceramics, sintered metals, rocks, concrete, and more.
Bubble point pressure
Wet membrane flow–pressure curve (wet curve)
Bubble point pore diameter (maximum pore size)
Dry membrane flow–pressure curve (dry curve)
Minimum pore size
Gas permeability
Mean pore size
Gas flux
Most probable pore size
Integrity evaluation
Pore size distribution
Fiber membrane burst pressure
Liquid permeability (liquid–liquid method)
Transverse gas diffusion performance evaluation
Liquid flux (liquid–liquid method)
Pore size measurement range:
Standard model: 0.012 µm–500 µm (gas–liquid displacement method); 5nm-50nm (liquid-liquid displacement method);Multiple sample cell configurations are available for samples of different sizes; custom-designed sample cells can be provided for special samples;
Equipped with a fully automatic vacuum-assisted wetting system, which significantly accelerates the wetting process and improves test efficiency by more than 50%;
Multiple wetting liquids available depending on the sample under test, including dedicated wetting liquid BSD-16 or other compatible wetting liquids;
High-precision dual flow sensors with segmented flow measurement, complementary measurement ranges, and automatic range switching;
High-precision dual pressure sensors with segmented pressure measurement; the system automatically determines and switches the appropriate pressure range via software control;
All-stainless-steel tubing with metal-to-metal hard sealing, providing excellent gas tightness, high pressure resistance, and corrosion resistance.