Home / Product / BSD...
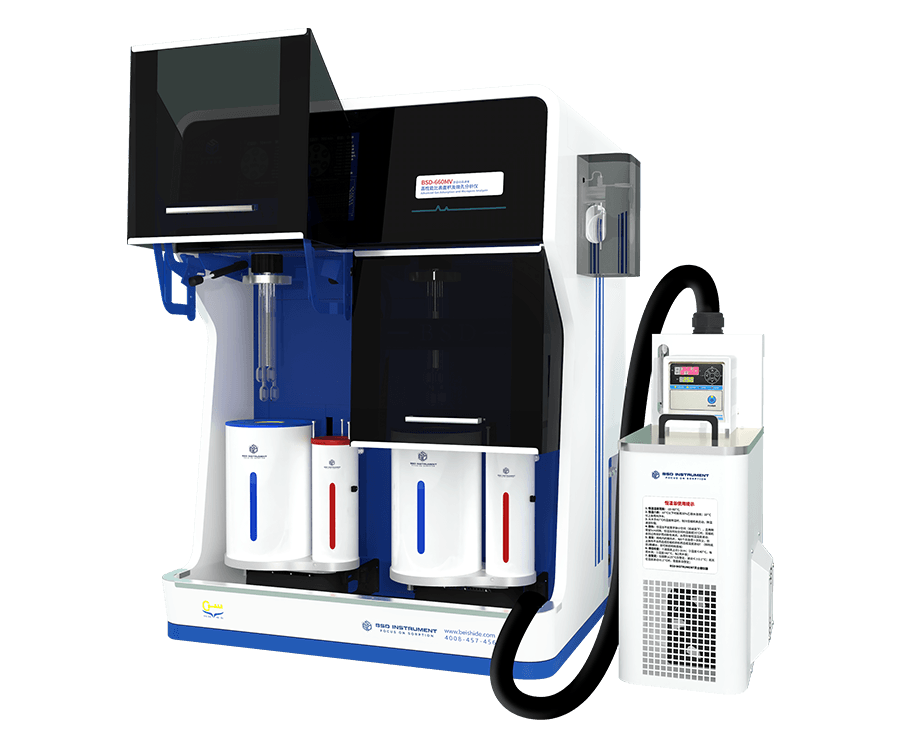
BSD-660MG AUTOMATIC GAS ADSROPTION ANALYZER
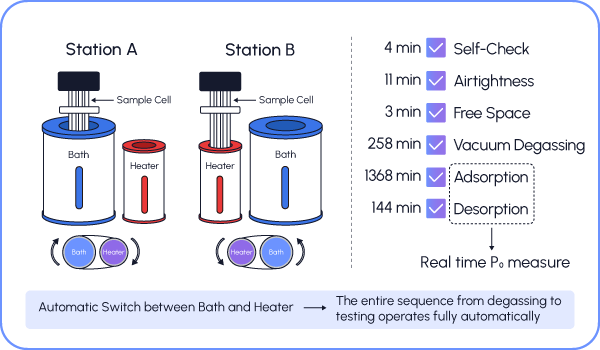
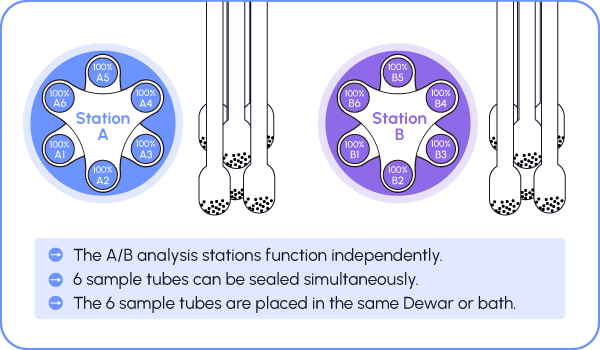
The versatile, high-performance instrument is designed for comprehensive gas adsorption testing. It supports the adsorption isotherm testing of conventional and flammable gases such as N2, O2, CO, CO2, H2, CH4, and C2H6. The analyzer provides full functionality for analyzing specific surface area, mesopores, micropores, and ultra-micropores. With high throughput capabilities, it offers 3, 6, 9, or 12 analysis positions and features fully automated operation, including degassing and testing cycles. The analyzer automatically cycles through material adsorption performance evaluations, providing reliable, repeatable results.
- Isotherm;
- BET surface area;
- Pore volume and pore size analysis;
- N2/ Ar/ Kr adsorption analysis;
- Regular gas adsorption analysis (E.g. N2, O₂, Ar, CO, CO₂)
- Flammable gas adsorption analysis (E.g. H₂, CH₄, C2H6)
- 3/6/9/12 analysis ports;
- Pore size 0.35nm-500nm;
- Full automatic In-situ activation& analysis;
- Vaccum System: 10^-2 Pa with mechanical pump, 10^-8 Pa with molecular pump.